Content of interest

Solutions presented at From Soya to Sustainability in Peterborough on Wednesday 22nd January included presentation of research carried out by SRUC, The James Hutton Institute and Agrii and the…

Revised figures reveal the full extent of the savings that would be made possible that increasing pulse production and displacing imported soya could bring.

Including legumes in the arable rotation clearly has the potential to lower environmental footprints, said Prof Pete Iannetta of The James Hutton Institute. “It’s not just greenhouse gases. There’s…

The 1000FARMS project is an initiative aimed at enhancing agricultural practices through extensive on-farm research and data collection. Our aim is to implement an Africa-wide network for on-farm…
1

The industry-wide OSR Reboot is driving a fresh start for oilseed rape production in the UK, tackling the challenges faced by growers in recent years. This groundbreaking initiative is fostering…

Putting farmers at the heart of innovation is key to getting the right technical solutions to their challenges.

Technical guide publshed by BASF in collaboration with ADAS, NIAB, SRUC and Teagasc on how to grow barley

Scientific paper in Big Data & Society by Monja Sauvagerd, Maximilian Mayer & Monika Hartmann of University of Bonn.
3
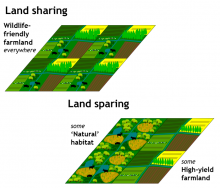
Are environmental benefits (carbon, biodiversity...) best served by sharing agricultural land with nature, or by maximising yield in some areas to spare tracts of land exclusively for nature in other…
2

On Farm Experimentation (OFE) is increasingly being recognised as having transformative power in improving performance in agricultural systems across the world.
3
Agri-TechE is a not-for-profit, independent membership organisation dedicated to advancing agricultural innovation and sustainability.
We take pride in our decade-long commitment to transforming…
2

Integrated Pest Management focusing on disease control in cereals
Link to video series playlist on YouTube
4

The Yield Enhancement Network (YEN) was launched in 2012 to support and energise on-farm learning-by-sharing and thus to enhance farming progress.
1

Cereal diseases affecting wheat, barley, oats, rye, triticale and maize can be caused by a variety of factors, including fungal, bacterial or viral infections, pests and insects, and environmental…

The extent to which disease develops in a crop is a balance between the likelihood of infection (i.e. disease pressure) and the ability of the crop to resist or avoid infection (i.e. field resistance…

Introduction
Over the last few months at FCT, we have seen an increase in the interest in understanding the impact on greenhouse gas emissions of adopting more regenerative farming practices.
As a…

The two key objectives of this work are to identify the best scenario for optimizing environmental impact and financial return for farmers and to determine the carbon cost-benefit of transitioning to…

With climate unpredictability increasingly impacting the agricultural sector, the UK’s farming landscape is undergoing a novel transformative shift. Here, Sarah MacAfee, Technical Officer for LEAF…

The IPMWORK network connects farmers and advisors across Europe. Developed based on LEAF and other existing networks, a series of IPM Hubs have supported farmers advancing their IPM programmes. …

As part of the development of the IPM Decisions platform, we carried out additional research and development both on the technical and social aspects relating to improving access to and uptake of…

